It helps with making decisions inside the company and in dealing with investors. This document meets SEC rules and is clear about a company’s financial health. Good accounting keeps a business financially comment: the importance of accounting comparability solid and ready for the future. After the post closing trial balance is finished and checked for any mistakes, any reversing entries that are needed can be made before the next accounting period begins.
When to use trial balances
Since these are determined to be temporary accounts, it contains no sales revenue entries, expense journal entries, no gain or loss entries, etc. As part of the closing process, the balances in these movements to the retained earnings account. The unadjusted trial balance is the first draft of the trial balance after the balances are posted in the ledger to prepare a financial statement. The purpose is to test the debit and credit accuracy after the recording phase. A post-closing trial balance ensures that all temporary accounts have been closed and that the company’s books are balanced.
Three Types of Trial Balance

Knowing the difference between temporary and permanent accounts helps in understanding their roles in accounting. Temporary accounts record revenues and expenses, resetting yearly. Permanent accounts carry forward their balances, crucial for financial analysis and assessing a company’s worth. A pre-closing trial balance shows all current account balances.
How to Prepare a Post Closing Trial Balance
It might miss transactions omitted entirely from the books. There’s also a chance it’ll fail to flag entries incorrectly coded to the wrong accounts, which can ultimately lead to inaccurate financial statements. You record all your accounting transactions and post them to the general ledger, then assess the debit and credit totals.
- The main purpose is to test equality between debit and credit after preparing the adjusting entries.
- After the post closing trial balance is finished and checked for any mistakes, any reversing entries that are needed can be made before the next accounting period begins.
- By providing a snapshot of all ledger accounts within a given accounting period, the trial balance helps business owners and accounting teams in reviewing accuracy.
- As mentioned above, it ensures that no temporary accounts are remaining and all debit balances equal all credit balances.
- The biggest goal of a trial balance is to find accounting errors and transposition errors like switching digits.
The Income Summary account is where these entries are summarized, reflecting a business’s profit. When a fiscal year ends, net income goes to retained earnings. This shows how a company plans to distribute profit in the future. The post-closing trial balance highlights only these permanent accounts, which are crucial for understanding a company’s equity. It’s crucial to know all balance sheet accounts with balances that aren’t zero.
Deferred Tax Assets – Definition, Example, and Why the Deferred Tax Asset Arises
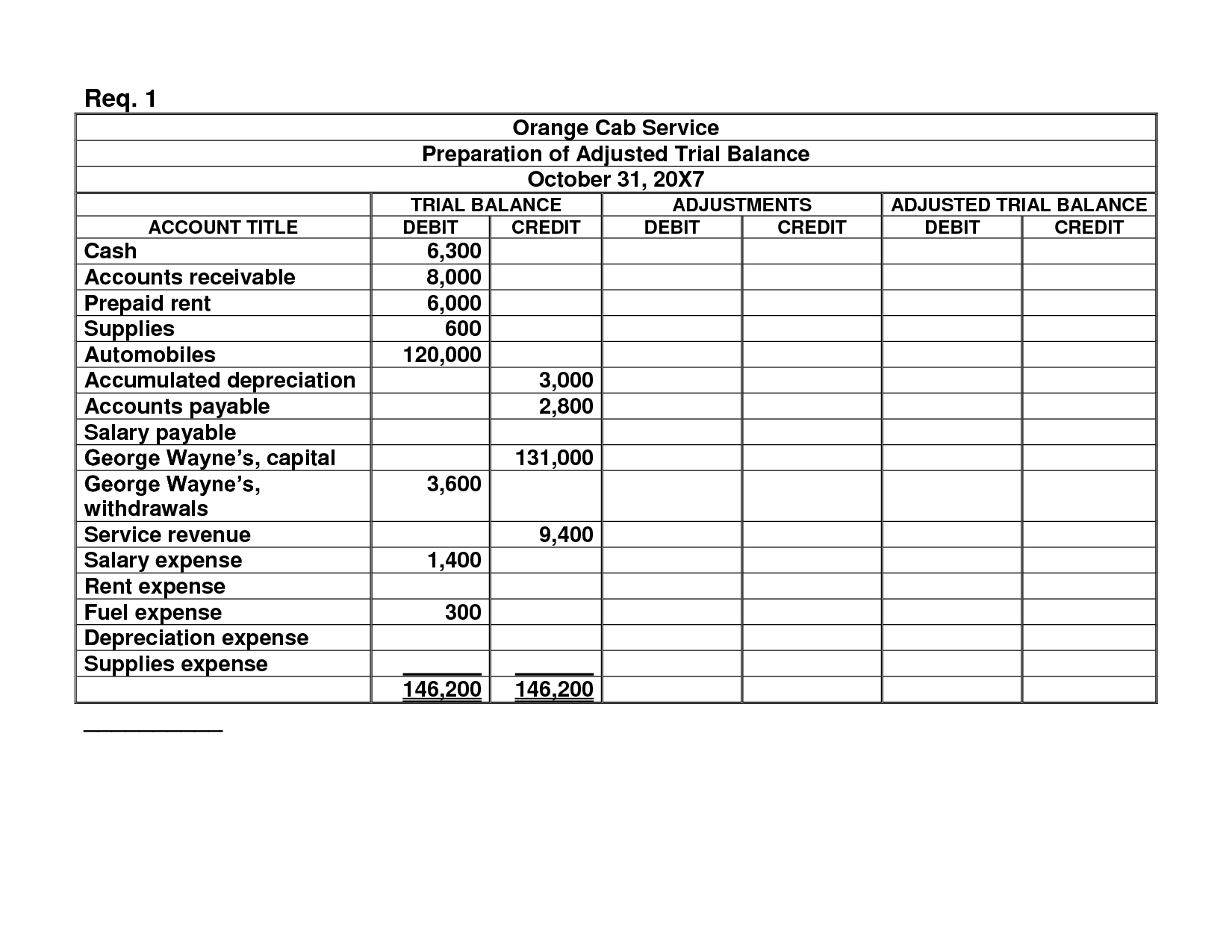
Before that, it had a credit balance of 9,850 as seen in the adjusted trial balance above. You probably noticed that a post closing trial balance looks a lot like a balance sheet in the format of a trial balance. In the middle column, you will place debit balances for every account, and in the rightmost column, you will place all credit account balances. Its key aspect is that it’s done after the period is closed, hence the name. Notice the middle column lists the balance of the accounts with a debit balance, while the right column has balances for credits.
Compiling a post closing trial balance is essentially the same as for unadjusted and adjusted trial balances. The main purpose of PCTB, as you know, is to make sure the credits and debits are balanced, and it’s the last effort before closing the reported period for good. Unlike the usual Trial balance, there are no unadjusted or adjusted variations, it’s all done in one go. At the end of the day, they all serve one purpose – to ensure everything in the ledger is accounted for properly. While a post-closing trial balance and an adjusted trial balance both serve as important financial reports for a company, their purpose and content differ. Finally, the accountant prepares the post-closing trial balance by listing all accounts with their updated balances after the closing entries have been made.
Adjusted trial balance is key for an exact post-closing trial balance. This step in the accounting cycle needs detailed use of accrual accounting rules to show real financial status. Accruals, showing earned revenues or incurred expenses, are noted even without cash transactions. Adjustments ensure prepaid expenses are spread out as needed, and depreciation on assets is rightly expensed. It ends the period with balanced entries, thanks to smart software.